The plastics industry has a history of complicated manufacturing processes. The procedure to melt plastic stock, transfer it to a die, then hardens to form the product is a process that cannot really be paused or interrupted.
This article discusses ways to correct power interruptions for plastic extrusion manufacturing processes.
Power Issues Affecting the Plastic Extrusion Process
Various power anomalies affect the plastic extrusion process in different ways. Below are some different power issues affecting today’s plastic extrusion facilities.
Power Outages
A complete
power outage will absolutely interrupt the plastic molding process. Regardless of which state the mold is in, once it is past melting should you interrupt the power, your process material will harden and will need to be cleaned and re-started. These are major events for plastic extrusion companies. A company will spend many hours if not shifts cleaning out the faulted process, and ready it to re-start.
Voltage Spikes
Uneven voltage situations, sags on the grid and voltage swells or spikes can also affect the plastic extrusion process in the same way a power outage can. Voltage spikes whether from lightning, stray voltage, or ramping up and down of larger equipment loads can also wreak havoc on plastic forming processes. Each time the voltage spikes the amperage will dip, and vice versa when the voltage sags the amperage spikes. This will wear on all pieces and parts of mechanical equipment, also very much wears process controls equipment until failure. You will not always see these event with the naked eye.
Voltage Sags
The increasing tax on our electrical grid and power demand continues to cause brownouts and
sags. Rolling brownouts and sags are not derived at the electrical utility, however, they come about along the distribution line. You are always subject to the affects of these power issues, and it is not that the utility company can necessarily do anything about it for you. Sags can be quite long in durations, again not visible to the naked eye. But pro-longed voltage sagging will directly raise amperage and burn on equipment, boards, processors, and controls.
Sags and spikes may not always knock equipment offline, however, the changes in voltage directly affect the operation and life of your plastic extrusion process equipment and controls.
Ways to Correct Power Interruptions for Plastic Extrusion
The following are different technologies that may correct or “fix” facility issues that are facing power related problems in the plastics industry. There is no magic bullet, but there are definitely measures that can be taken to prevent downtime.

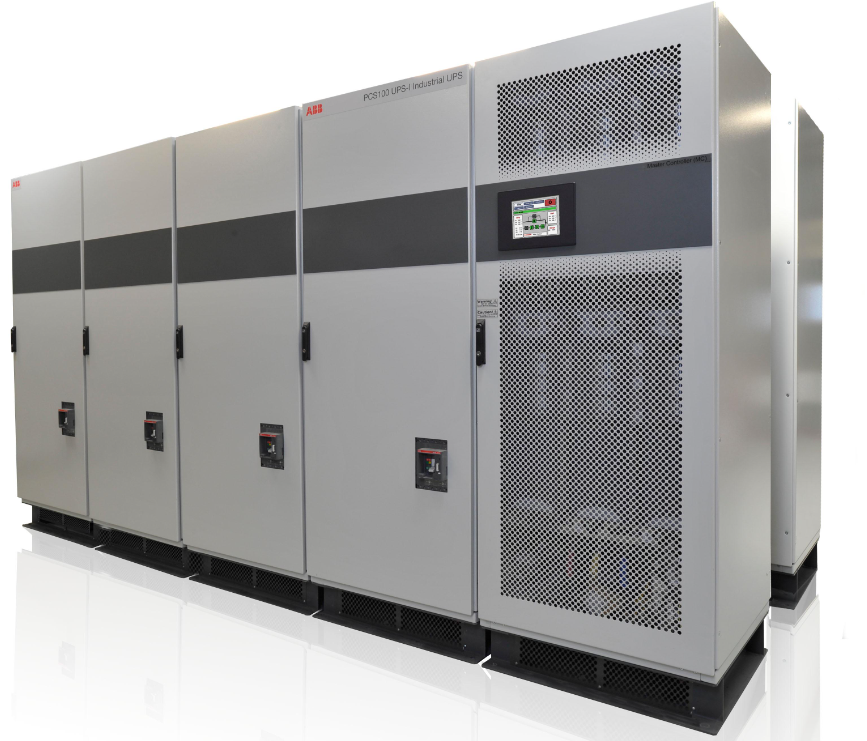
Industrial UPS Systems
An
Industrial UPS System is specifically made for mechanical environments such as plastics industry. Typically made with internal transformers and capacitors sized for taking on larger industrial or high inrush current loads. A typical data center or IGBT type UPS system built for computer processors is not usually a good fit for the harsh environment of a plastic extrusion plant or other manufacturing loads.
(AVC) Active Voltage Correction System
99% of power issues affecting process controls and manufacturing are associated with sags, surge and spiking voltage events. A properly designed AVC – Active Voltage Correction System can provide 100% protection against all these issues. An AVC system can correct a single-phase sag that may dip 30% of nominal voltage. It can correct all 3 phase sags up to 30% of nominal. It is an absolute must for plastic extrusion process environments.
(AVR) Active Voltage Regulator
Much like an AVC system, the AVR holds a tighter input voltage window it is willing to accept. Much like a Voltage Conditioner, the AVR system will take a varying voltage and tighten it up to within +/- 5% nominal voltage. It will not take care of larger sags or swells. If power in your facility is not the worst, but you wish to tighten the voltage and operational window for all your plastic process controls and equipment, then and AVR is an inexpensive solution to provide that type of operational integrity.
About Voltage Correction
Voltage Correction is a provider of power correction services globally. Please contact your
Voltage Correction representative to discuss power correction options for your facility and plastics operation. Call 855-240-6776