Backup Power Requirements for Bitcoin Mining Industry
12 August 2024
Share this article:

When considering the electrical requirements for a bitcoin mining operation you must weigh several factors to install an efficient delivery of power. Also considering the risks of power failures, sags and interruptions to choose the correct technologies for your bitcoin mining farm.
By implementing an effective electrical power strategy can determine the success of your bitcoin mining operation.
Power Utility Options for Bitcoin Mining
Bitcoin mining has captured interest in locations that provide renewable resources. Not only for the cost of input (electricity), but also to lessen the impact on climate change. Many farms are seeking to locate in areas such as Texas that provide much renewable resource by way of wind farms. Others seek cost savings by expending less cooling dollars by locating in Greenland, or northern climates. A large portion of cost to produce bitcoin is expended cooling the bitcoin mining operations. These types of climates provide lower PUE (Power Usage Effectiveness) or more output vs. the electrical input cost. All of these choices, however, put the facility in the crosshairs of variable power disruptions. The mining owner will have to decide if spending capital dollars on the front end is worth it to eliminate power interruptions during operation.
Ways to Correct Power Interruptions for Bitcoin Mining
As discussed, the type of power input or source of power has much to do with how much protection is needed from variable voltage swings, or power outages. Bitcoin operations will need to weigh the cost to correct power in capital expenditures vs. the operational effects it will have on uptime in operations. The following are several ways to correct power issues.
Industrial Uninterruptible Power System (UPS)
A fully industrial UPS system with transformer-based technology would be a full isolation of the utility power source and the bitcoin mining loads. A choice of Pure Lead, VRLA, or Lithium-Ion batteries can be installed for specified runtimes. Typically a system will be sized for 10-20 minutes of backup battery runtime. This would correct 98% of normal voltage sag, and momentary interruption scenarios. Also provide for sequential load shedding upon an outage event, which runtime could be extended longer for more critical components. UPS Systems of this type also protect and extend the life of bitcoin mining components. Constant voltage swings provide wear and tear on expensive bitcoin mining equipment causing premature failures, and higher operational expenses over time. The UPS provides a clean, sterilized power output for the mining operation.
Industrial UPS and Generator
A UPS described above with a shorter duration battery yet combined with a backup generator with automatic transfer switch. This combination would provide for extended, or unlimited runtime provided there is fuel available for the generator. The UPS will isolate all the voltage variations and sags with it’s power sterilization technology. When an outage occurs the backup generator system will automatically switch over via the (ATS) and be the main source of power.
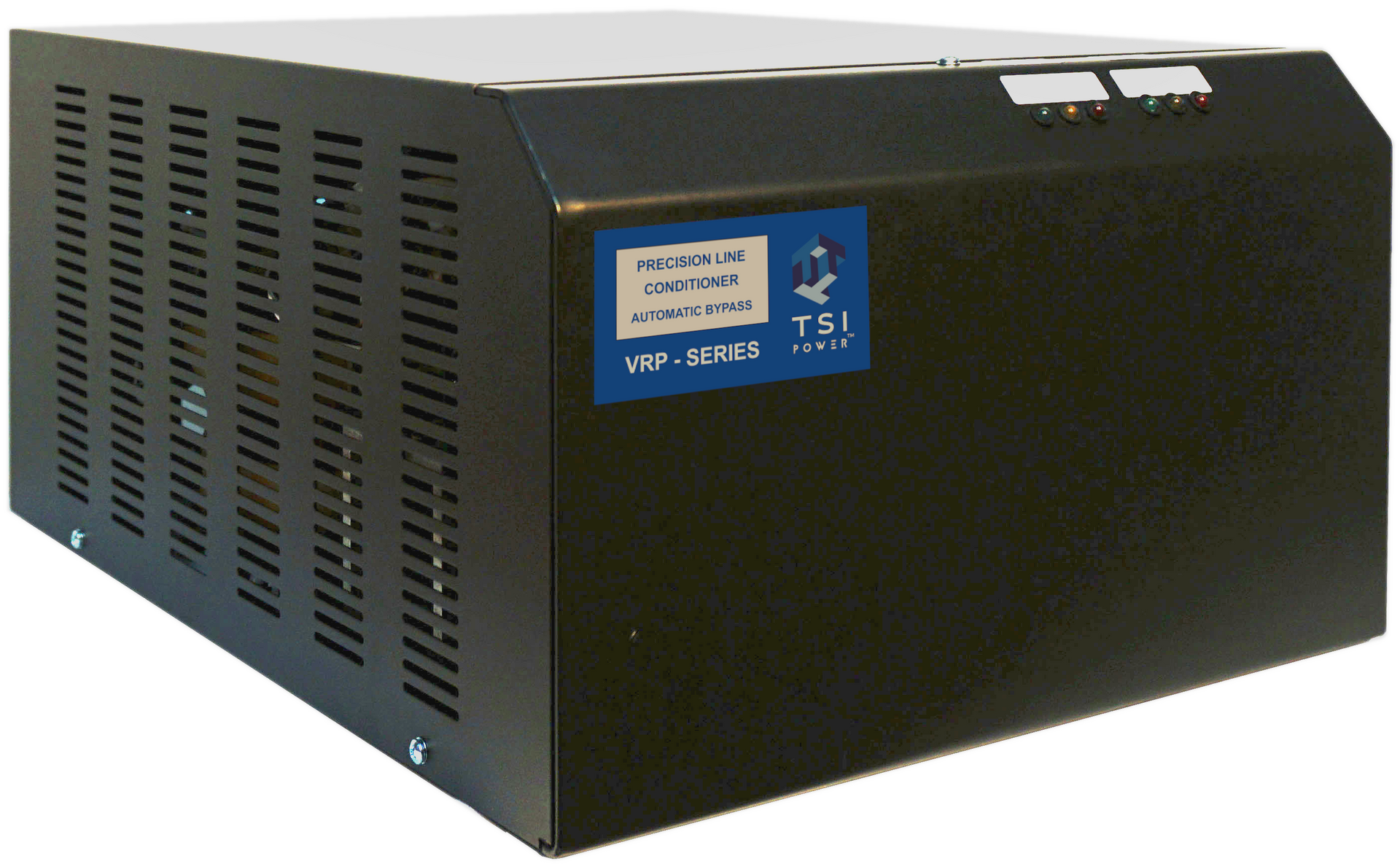
Voltage Correction or Conditioning
If the utility power source is reliable and relatively free of power outages and interruptions. You can correct or stabilize power without battery storage or backup generation. Voltage Correction and/or Conditioning can provide for the regulated voltage output that will provide clean corrected power for your bitcoin mining components, without the higher cap ex cost for the additional storage or runtime. This option at a minimum would be suggested for all bitcoin mining applications.
PUE Efficiency and Backup Power Choices for Bitcoin Mining
Choosing a backup power system, whether it be a UPS Systems, Voltage Correction System, or emergency backup generator should not materially impact your PUE (Power Usage Effectiveness) in your mining operations. UPS systems today provide up to 99% efficiency to operate 100% of the time. During occasional battery charging periods there will be additional amperage draw on the system, but is very minimal. Most if not all of the UPS, Generator, Switching, and distribution is standby in nature. Therefore, the upfront Capital Expenditure will be the cost outlay and the operational PUE will not be affected by these systems. Your choice for backup would be to weigh the operational downtime effects of outages vs the upfront cost to prevent them. The larger effect on PUE would be the choices made for cooling options.
Should you Backup Bitcoin Mining?
The operational efficiencies that you gain long term and the quality of output from your mining equipment says you should invest at a minimum in a voltage stabilizing system. Should you want to completely avoid downtime scenarios, re-boots, and general labor costs to manage your site, then the investment into fully backed up bitcoin operations is extremely justified.
Voltage Correction is experienced in designing and installing electrical systems for the Bitcoin mining industry. We can help you choose the right system for your project. Please contact your representative to discuss opportunities to build out your electrical and mechanical systems for your Bitcoin Mining Operation.
Connect with Us: